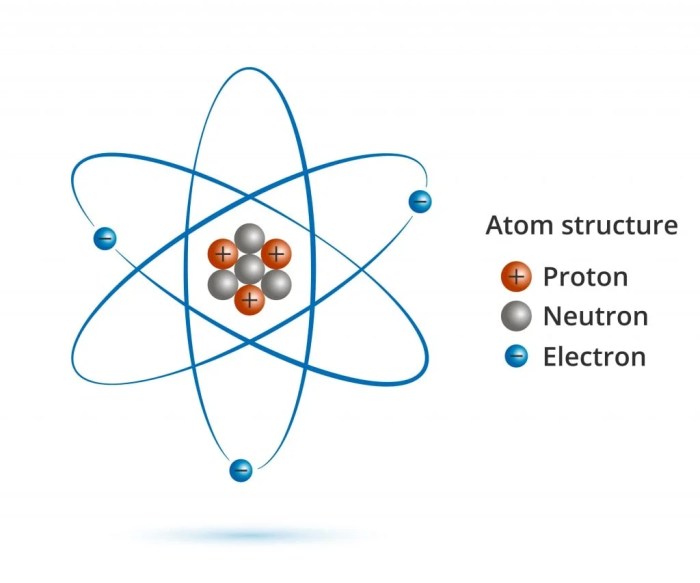
Draw five protons in the nucleus of the atom – As we delve into the heart of the atom, the nucleus, we embark on a captivating exploration of the fundamental particles that define its very essence. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of five protons, the enigmatic building blocks that shape the identity of elements and orchestrate the symphony of nuclear reactions.
Within the confines of the nucleus, protons reside as the architects of atomic identity, their presence dictating the element’s position on the periodic table. Their intrinsic properties, such as charge, mass, and spin, play a pivotal role in shaping the atom’s behavior and interactions.
Nucleus Structure: Draw Five Protons In The Nucleus Of The Atom
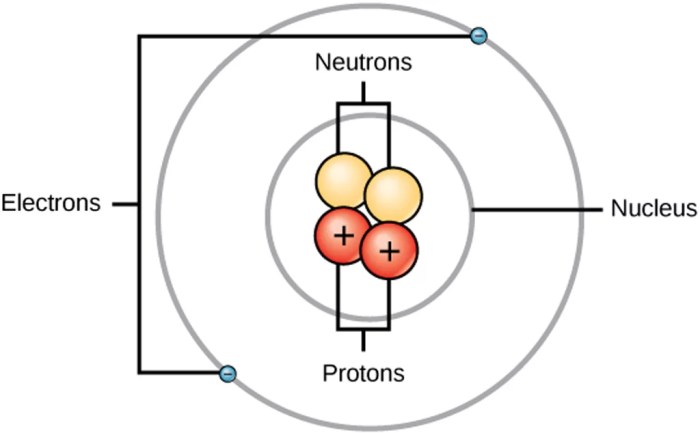
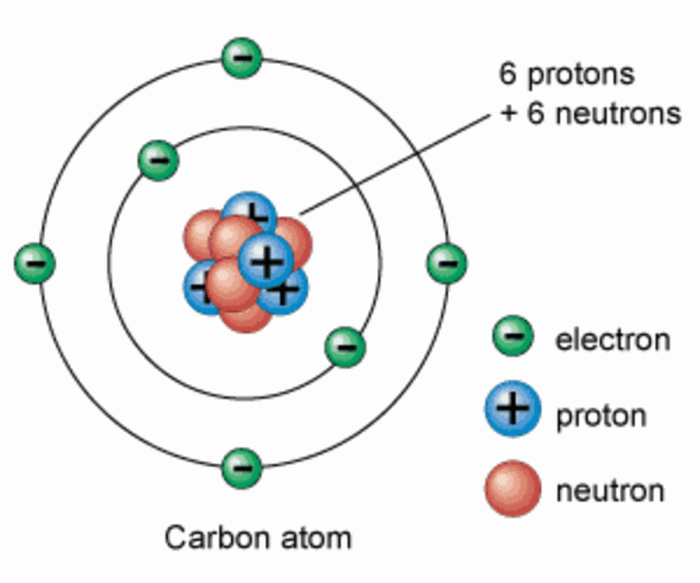
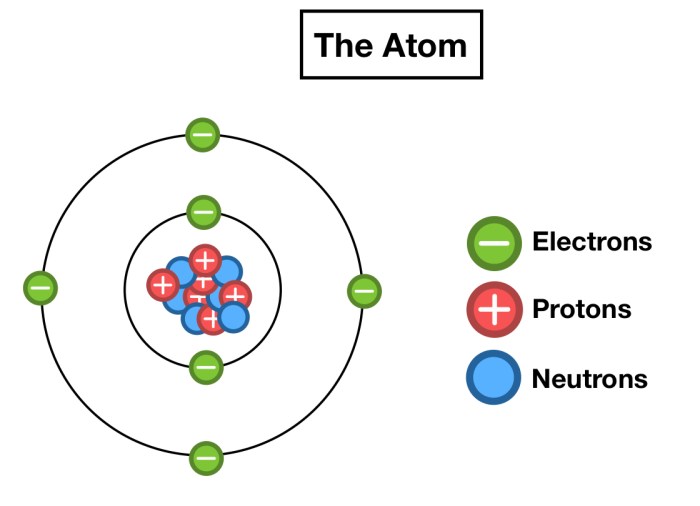
The nucleus is the central core of an atom, where protons and neutrons reside. Protons are positively charged particles that define the atomic number of an element. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus, and it determines the element’s identity.
Protons are arranged within the nucleus in a specific configuration, which varies depending on the element.
Proton Properties, Draw five protons in the nucleus of the atom
Protons possess fundamental properties that contribute to the structure and behavior of atoms. They have a positive charge of +1 elementary charge, a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), and a spin of 1/2. Variations in the number of protons within an element’s nucleus give rise to isotopes, which have different atomic masses but the same atomic number.
Protons play a crucial role in nuclear reactions and energy production. Nuclear reactions involve changes in the number of protons within the nucleus, leading to the formation of different elements. In nuclear power plants, controlled nuclear reactions release enormous amounts of energy through the process of nuclear fission.
Visual Representation
| Proton 1 | Proton 2 | Proton 3 | Proton 4 | Proton 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 |
Proton Interactions
Within the nucleus, protons interact with each other through electrostatic forces. These forces are repulsive due to the positive charges of protons. However, the strong nuclear force, a short-range attractive force, overcomes the electrostatic repulsion and stabilizes the nucleus.
The balance between electrostatic repulsion and the strong nuclear force determines the stability of the nucleus. In larger nuclei, the electrostatic repulsion becomes more significant, requiring a stronger strong nuclear force to maintain stability.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of protons in determining an element’s identity?
Protons play a crucial role in defining an element’s identity. The number of protons within an atom’s nucleus determines its atomic number, which in turn uniquely identifies the element on the periodic table.
How do protons contribute to the stability of the nucleus?
Protons possess a positive charge, which leads to electrostatic repulsion between them. However, the strong nuclear force, a powerful short-range attractive force, overcomes this repulsion and stabilizes the nucleus.
What is the concept of isotopes?
Isotopes are variations of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. Isotopes share similar chemical properties but may exhibit distinct physical properties due to their different masses.